

Coyote Dry Lake Meteorites
The Coyote Dry Lake meteorites are named after the California dry lake on which they were found, a large playa 20 miles NE of Barstow in San Bernardino County. For the past 10 years, over 250 chondritic stone fragments and individuals have been found at this locality. Every known find has been documented. Each of them has had its date-of-find, weight in grams, and GPS coordinates recorded. This information was reported to the Nomenclature Committee of the Meteoritical Society. Having supplied all of the required information, it was now possible to get provisional numbers assigned to each of the more than 250 finds.
The first known find from this locality was made by this author in 1995, but it wasn't classified until 1999. It was characterized as being "H5 S2 W3", as are the majority of the finds from this locality. But, over the years as finds were continually made, each would be closely scrutinized, and every specimen that was deemed "out of character" (from the original H5 S2 W3 stones) would be turned in for classification. Presently, there are nearly 50 of these specimens that have been classified. Although a proper pairing study has yet to be done, here is the breakdown of the current classifications:
21 - H5 S2 (most are "probably paired")
10 - H4 (1 group of whole individuals are "probably paired" and at least 2 other groups of "possibly paired" stones)
5 - H6 (1 group of whole, fresh stones are "probably paired" and another group of weathered stones are "possibly paired")
2 - H5-6 S2 br ("probably paired")
1 - H5-6 S4 br (unpaired)
1 - H3
2 - L5-6 S2-3 W1 ("probably paired")
2 - L6 S4 W5 ("probably paired")
1 - LL6
20% of all the known finds from this locality have been classified. This might be considered a high percentage, but in retrospect, an argument could be made that this may be a minimal percentage that should be undertaken to properly characterize a strewn field, as well as to detect any overlapping sporadics. And indeed, Coyote Dry Lake is a prime example of overlapping strewn fields. Having every known find properly recorded affords researchers an excellent opportunity for a proper case study of a "hot desert" area of dense accumulation/collection. The present endeavor of the current field workers is to determine the degree to which the overlapping strewn fields have been compromised by lateral transportation of the meteorites. In other words, is the pattern of finds representative of an unaltered strewn field, or does the pattern depict a broad stranding surface that the various meteorites have been stranded upon?
The recovery information for each of these classified stones were tabulated, and this table was submitted to the Nomenclature Committee. The name "Coyote Dry Lake" was approved by the Committee for these classified stones, as well as for the remaining 200 "provisionally numbered" finds. The name "Coyote Dry Lake" appears for the first time in print when published in the Meteoritical Bulletin #89 (2005).
A copy of the submitted table is shown below:
| Table n. | Ordinary Chondrite finds from Coyote Dry Lake, San Bernardino County, CA - dense collection area of the California Mojave Desert. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Mass | Found | Latitude | Longitude | Pcs | Class | Shock | WG | Fa | Fs | Wo | Cmt | Finder | Type | Info* | Main Mass | ||||
| (g) | mm/dd/yyyy | N35º | W116º | Stage | mol% | mol% | mol% | Spec (g) | holder * | |||||||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 001 | 338.00 | 5/25/1995 | 3.01 | 46.01 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.6+/-0.5% | Robert Verish | 22.7 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 002 | 106.7 | 12/13/1998 | 2.852 | 43.855 | 2 | H5-H6 | S2-S4 | W3-W6 | 19.6+/-0.2% | 16.1 | genomict breccia | Robert Verish | 22.1 | UCLA | Verish | |||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 003 | 255.72 | 12/21/1998 | 5.285 | 45.239 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.7+/-0.3% | Nick Gessler | 36.73 | UCLA | Gessler | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 024 | 2430.00 | 1/6/1999 | 4.290 | 46.323 | 2 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.8 | Nick Gessler | 20.23 | UCLA | Gessler | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 033 | 5220.00 | 1/13/1999 | 3.363 | 46.578 | 6 | H5 | S2 | W4 | 18.7 | Paul Gessler | 27.9 | UCLA | Gessler | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 040 | 344.00 | 1/16/1999 | 5.624 | 45.806 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W2 | 18.8 +/-0.?% | Probably paired to CyDL 063 | Robert Verish | 20.5 | UCLA | Verish | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 054 | 392.80 | 1/16/1999 | 4.600 | 44.800 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.7+/-0.3% | Robert Verish | 35.5 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 061 | 2134.00 | 1/21/1999 | 3.145 | 46.002 | 14 | H5 | S2 | W4 | 18.7+/-0.1% | Paul Gessler | 24.9 | UCLA | Gessler | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 063 | 67.61 | 1/21/1999 | 3.527 | 46.380 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W1 | 18.5 +/-0.3% | Probably paired to CyDL 040 | Paul Gessler | 15.1 | UCLA | Gessler | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 064 | 1364.31 | 1/21/1999 | 3.490 | 46.458 | 6 | H5 | S2 | W5 | 18.4 +/-0.3% | Paul Gessler | 25.2 | UCLA | Gessler | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 067 | 412.05 | 1/21/1999 | 2.289 | 45.186 | 2 | L6 | S3 | W5 | 25.4 +/-0.?% | Probably paired to CyDL 228 | Nick Gessler | 25.5 | UCLA | Gessler | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 080 | 278.10 | 1/21/1999 | 4.441 | 45.670 | 4 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.6 +/-0.?% | Nick Gessler | 20.5 | UCLA | Gessler | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 105 | 61.5 | 4/17/1999 | 3.044 | 46.019 | 4 | H5 | S2 | W4 | 18.9 +/-0.5% | Gerry LaBarbera | 15.8 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 110 | 68.02 | 4/17/1999 | 2.775 | 44.128 | 3 | H4 | S3 | W3 | 19.2 | Gerry LaBarbera | 13.5 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 115 | 1369.00 | 7/4/1999 | 3.519 | 46.123 | 21 | H5-H6 | S2 | W3-W4 | 19.0+/-0.6% | br, Probably paired to CyDL 151 & 152 | Nick Gessler | 27.4 | UCLA | Gessler | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 116 | 4.4 | 7/22/1999 | 3.508 | 46.140 | 1 | H6 | S2 | W4 | 18.3+/-0.3% | Robert Verish | 4.4 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 117 | 162.00 | 7/23/1999 | 3.006 | 44.666 | 1 | H3 | S2 | W3 | 18.0+/-0.4% | Robert Verish | 33.2 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 119 | 3.20 | 7/24/1999 | 2.289 | 45.186 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W5 | 18.7+/-0.1% | Robert Verish | 3.2 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 120 | 18.5 | 8/7/1999 | 3.536 | 46.123 | 1 | H5 | S1 | W4 | 18.8+/-0.3% | Gerry LaBarbera | 17.95 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 121 | 14.2 | 8/7/1999 | 3.568 | 46.110 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W2 | 18.7+/-0.?% | Gerry LaBarbera | 2.8 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 129 | 140 | 2/11/2000 | 4.150 | 45.012 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.60% | Robert Verish | 20.6 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 130 | 6.1 | 2/11/2000 | 4.071 | 44.964 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W3 | 19.00% | Robert Verish | 5.9 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 132 | 17.4 | 2/19/2000 | 4.217 | 44.908 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W3 | 18.60% | Gerry LaBarbera | 17.2 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 134 | 117.5 | 4/8/2000 | 5.550 | 45.650 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 19.2+/-0.9% | James LaBarbera | 22.5 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 138 | 18.30 | 4/8/2000 | 3.170 | 45.987 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W5 | 18.5+/-0.3% | James LaBarbera | 17.1 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 139 | 10.4 | 4/8/2000 | 3.170 | 45.923 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W4 | 19.1+/-0.4% | Gerry LaBarbera | 3.1 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 142 | 32.22 | 5/5/2000 | 4.035 | 44.912 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W3 | 18.9+/-0.8% | Robert Verish | 10.2 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 151 | 90.04 | 2/16/2001 | 3.361 | 43.421 | 1 | H6 | S2 | W5 | 19.3+/-0.2% | br, Probably paired to CyDL 115 & 152 | Rob Matson | 22.92 | UCLA | Matson | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 152 | 10.84 | 2/16/2001 | 3.364 | 43.419 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W4 | 19.0+/-0.3% | br, Probably paired to CyDL 115 & 151 | Rob Matson | 2.79 | UCLA | Matson | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 153 | 13.87 | 3/7/2001 | 4.417 | 45.823 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.8+/-0.7% | Rob Matson | 3.99 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 155 | 17.02 | 4/15/2001 | 4.108 | 46.143 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W2 | 18.6+/-0.2% | Rob Matson | 5.07 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 159 | 17.70 | 11/16/2001 | 3.519 | 46.123 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W4 | 18.6+/-0.3% | Robert Verish | 5.8 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 160 | 76.88 | 1/13/2002 | 3.691 | 45.777 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W1 | 17.9+/-0.?% | Rob Matson | 15.44 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 162 | 9.87 | 1/13/2002 | 4.681 | 46.066 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 16.1 | Rob Matson | 2.15 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 163 | 16.66 | 2/8/2002 | 4.200 | 46.200 | 1 | H5 | S3 | W5 | 18.3+/-0.?% | Rob Matson | 3.7 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 164 | 43.00 | 2/8/2002 | 3.501 | 46.442 | 1 | H5 | S2 | W3 | 18.3+/-0.?% | Rob Matson | 10.21 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 165 | 42.57 | 2/18/2002 | 4.133 | 45.718 | 1 | L6 | S3 | W4 | 24.4+/-0.?% | Rob Matson | 9.1 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 175 | 36.35 | 12/13/2002 | 3.285 | 45.259 | 1 | H6 | S1 | W3 | 18.1+/-0.1% | Rob Matson | 9.09 | UCLA | Matson | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 176 | 187.55 | 2/1/2003 | 3.271 | 43.803 | 2 | H6 | S3 | W1 | 18.4+/-1.1% | Probably paired to CyDL 221 | Rob Matson | 19.58 | UCLA | Matson | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 221 | 54.31 | 12/13/2003 | ~3.75(?) | ~43.35(?) | 1 | H? | S3 | W1 | 18.1+/-?.?% | Probably paired to CyDL 176 | Adam Hupe | 12.1 | NAU | Hupe | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 194 | 1.47 | 1/9/2004 | 5.303 | 45.170 | 1 | L6 | S3 | W1 | 23.8+/-0.5% | Probably paired to CyDL 222 | Rob Matson | 0.65 | UCLA | Matson | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 222 | 22.5 | 5/8/2004 | 2.405 | 45.332 | 1 | L5 | S2 | W1 | 23.7+/-0.1% | Probably paired to CyDL 194 | Gerry LaBarbera | 4.85 | UCLA | Verish | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 223 | 512.00 | 5/8/2004 | 2.305 | 45.491 | 8 | L6 | S4 | W5 | 24.9+/-0.4% | Probably paired to CyDL 067 | Gerry LaBarbera | 30.6 | UCLA | Verish | ||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 230 | 16.36 | 6/13/2004 | 5.375 | 45.004 | 1 | H6 | S3 | W3 | 19.1+/-1.2% | 16.4 | 1.1 | Rob Matson | 3.5 | UCLA | Matson | |||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 235 | 81.4 | 7/10/2004 | 3.377 | 44.026 | 1 | LL6 | S4 | W2 | 28.1+/-0.1% | Robert Verish | 16.4 | UCLA | Verish | |||||||
| Coyote Dry Lake 249 | 71.8 | 10/24/2004 | 5.250 | 44.800 | 1 | H4 | S2 | W2 | 18.1+/-0.4% | 15.9+/-0.2% | Tak Kunihiro | 14.22 | UCLA | finder | ||||||
| * = the abbreviations and words used here in italics are defined in the Meteoritical Bulletin. | ||||||||||||||||||||
No doubt, the high number of finds from one locality will garner some deserved attention, but I feel that something else just as significant needs to be recognized here, as well. What needs to be understood is that in order to get 100% of the 250 known finds from this locality recorded, it took the collaborative effort of 16 individual finders. Other than myself, as an acting principal investigator, there was no formal institution or university that organized this effort. The findings that you read here are the result of a concerted, yet volunteer effort by individuals searching independently for meteorites. Granted, Dr. Alan Rubin of UCLA spent many hours in the lab characterizing nearly all of the classified finds, but it was all of the (non-professional) field workers (meteorite hunters) that volunteered their time and effort to record recovery data that made it possible for all of these Coyote Dry Lake meteorites to be tabulated, so that they could be approved by the NomCom, and ultimately published in the Meteoritical Bulletin.
Credit needs to be given to all of these Coyote Dry Lake meteorite "finders".
1998 1999-2000 2001 2003 2004 Robert Verish Nick Gessler Rob Matson Peter Utas Alexander Utas Gerry LaBarbera Lisa Leupp Matson Jason Utas Andrew Utas James LaBarbera Adam Hupe Tak Kunihiro Paul Gessler Steve Drummond Ora Gessler Greg Hupe
Again, I would like to reiterate that the above finders searched Coyote Dry Lake independently. Meaning that when Nick Gessler (1999), Rob Matson (2001), Peter Utas (2003), and Adam Hupe (2003) made their initial find at Coyote Dry Lake, they were working independently and had no prior knowledge of previous finds. In time teams would develop. As can be seen by the names above, teams were comprised, for the most part, of family members. (And in the case of the Utas family, we have finds made by all 3 generations!!!) By not being biased, at least initially, by the knowledge of previous finds (or where on the dry lake they were made), each succeeding finder appeared to make good use of their "beginner's luck". But in time, the teams would eventually collaborate and would share in each other's good fortunes. And when it came time to submit everyones results to the Nomenclature Committee, the data compilation was not as problematic as might be expected with so many finds and finders.

Why have so many meteorites been found at Coyote Dry Lake, and can we expect to find just as many at other dry lakes in the Southwestern United States? The answer to both of these questions is linked to the geologic history of the Mojave Desert. The past 30,000 years have produced a unique geologic history for this part of the Mojave Desert, and as a result, makes Coyote Dry Lake very special. It is very likely that the special conditions that exist at Coyote Dry Lake may be present at only a very few dry lakes.
Researchers have determined that the Mojave River changed its direction of flow during the Late Wisconsinan (N. Meek, 1999) and started to flow back inland. Between 30 to 21.5 ka BP, Harper Valley was the terminus for the Mojave River. At that time the climate was much wetter than it is now, and a large lake formed in that area, Lake Harper. During that same time period, the Mojave River would intermittently discharge into the Coyote Basin. This produced Lake Coyote, the northern embayment of the even much larger Lake Mannix. Lake Coyote last formed about 11.8 ka BP. The Mojave River would never again flow into this basin. It would only take several decades for Lake Coyote to dry up, producing the present playa known as Coyote Dry Lake. The Coyote Basin, now starved of the sediment from the Mojave River, would start the process of deflation on this playa that would continue to this present day. Any meteorites that may have fallen into Lake Coyote, or into the soft clay of the Coyote playa, would now start to become exhumed.
The details of the above "geologic history" are debatable, but for a good review about the of the latest findings, go to Mojave Desert Symposium (Norman Meek) 2004.
But this very specific geologic history is the main point for why Coyote Dry Lake is considered a "very special condition" and why the high number of meteorite finds may be a unique case.
Yet, this begs the question, given the similar geologic history, why doesn't Harper Dry Lake have a similarly high number of found meteorites? And here is my explanation: there has been a rapid change that has recently occurred at Coyote Dry Lake (at least "rapid", geologically speaking). In speaking with long time residents and visitors to Coyote Dry Lake from over 40 years ago, there is the oft-repeated statement of "the lakebed was much, much softer than it is now, and extended from shoreline to shoreline." Ron Hartman had the same observation when he attempted to search for meteorites on this lake back in the early 1970s. Indeed, along the margin of this dry lake there are remnant patches of "abandoned" lakebed sediments that are higher standing (elevation wise, as well as stratigraphically) by nearly 2 meters than the rest of the present, hard-packed, lakebed surface. This sediment is composed of a very soft, expansive, distinctively light-colored silt. If indeed, this much sediment found a way to exit this playa in just 40 short years, then this rapid erosion would greatly improve the rate of any buried meteorites being exhumed. This, in itself, is enough to explain why Harper is not like Coyote Dry Lake.
Speaking for myself, I can only recount my observations on that day in May of 1995, the first time that I visited Coyote Dry Lake (the very first time that I ever drove on any dry lake). My main intent was to take a short cut to the Interstate, but that proved to be a bad idea when I found myself having to brake for deep ditches that were far too numerous to make driving on this playa practical. (These "ditches" were actually subsidence features just like those that form the giant polygonal patterns on Lucerne Dry Lake in Lucerne Valley, CA, and Red Lake in Mohave Co., AZ.) I also observed that there were a lot more rocks, pebble- and even cobble-sized, than I would have expected on a clay lakebed. Another thing that I remember was there were a large number of rocks that were "pedestaled", that were sitting on top of a column of lakebed clay, which I observed as being evidence of a peculiar, accelerated erosion. In fact, the first meteorite find from this lake was one of these "pedestaled" stones that had slipped off of its pedestal, and was now sticking vertically out of the ground. But the point that I want to make is that when I returned to this dry lake 3 years later, these "numerous ditches" had disappeared! They were all gone, and most likely had been filled in during storms. This may be the mechanism that accelerates the exhumation of buried meteorites. In any case, this was my first of many observations of dynamic, short-termed processes of change on dry lakebed surfaces.
If you are wondering about the 3 year hiatus in my visits to Coyote Dry Lake, the explanation is documented here:
Meteorite-List post, dated Friday, November 27, 1998
Soon, after this story was posted, began an intensive meteorite-recovery effort.
The image below depicts the preliminary results after just the first year (1999) of field work. Although many more finds were made in the succeeding years, there are strong indications that the majority of these subsequent finds had not yet been exhumed, as of late 1999. Evidence of geomorphic changes to the lakebed has been observed which suggests that this agrading and degrading of certain areas are alternatingly burying and exhuming meteorites. A series of images, like the one below, depicting a years worth of meteorite finds would most likely show this alternating pattern.
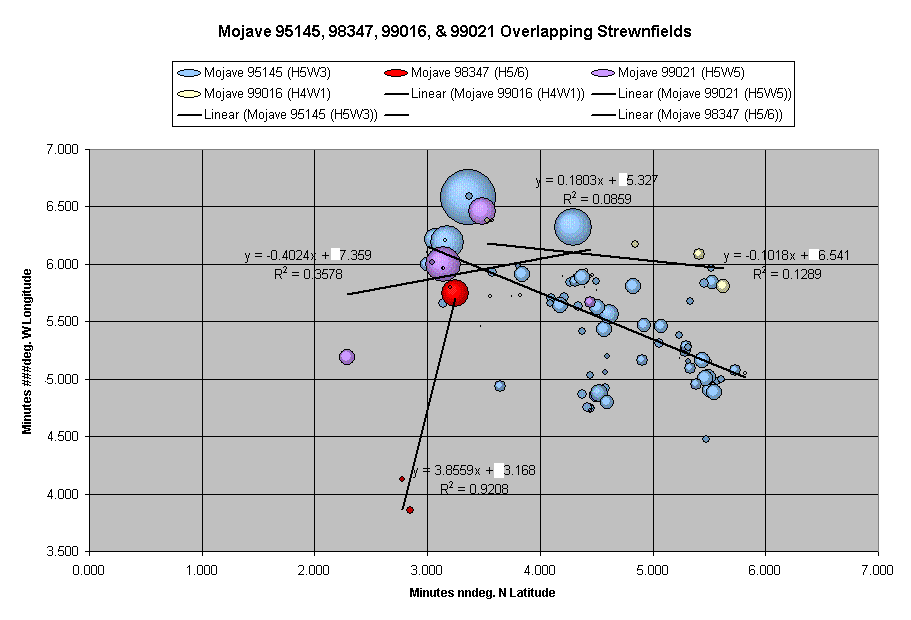
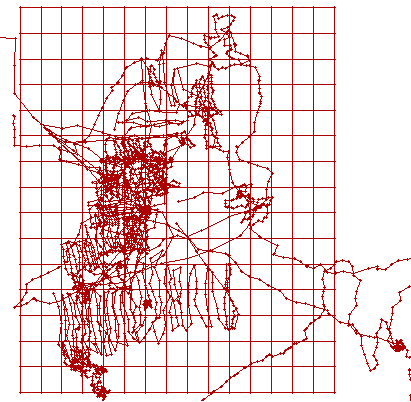
The next image, below-left, depicts the accumulated tracklogs recorded by Rob Matson on his GPS during his 2001 fieldwork. This has the obvious benefit of showing Rob the areas that he has conducted a grid search, versus the areas that he still needs to search. An added benefit of keeping such detailed records is that, when Rob revisited these searched areas 2 years later, he was able to determine that his new finds were not those that he "missed", but that they must have been exhumed over that 2 year period. Keep in mind that the other searchers kept tracklogs, as well. For comparison, the image, below-right, depicts the accumulated GPS tracklog files recorded by the Verish M-Recovery Team during their 2003 fieldwork.
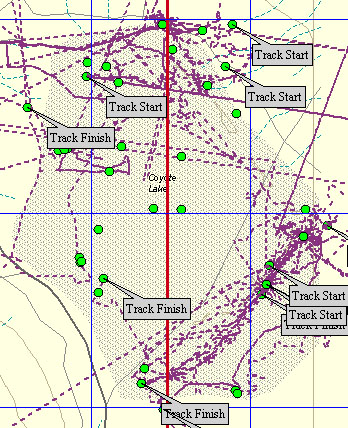
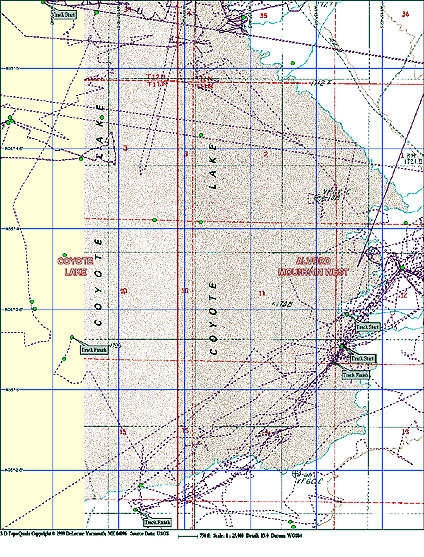
The next image, below-left, depicts Rob Matson's accumulated tracklogs up to the end of 2004, but overlain onto a topo map. And the image, below-right, depicts the above GPS tracklog files recorded by the Verish M-Recovery Team, but shown on a topo map at a smaller scale for more detail.

Although the high number of recorded finds from Coyote Dry Lake may be perceived as an exception, the following letter (referenced below) from Jeff Grossman (2005) shows that the documentation of these meteorites is in complete conformance with "2) the rules for handling paired meteorites from dense collection areas". Far from being an exception, Coyote Dry Lake meteorites are, in fact, following the rule. And there are other localities that are "areas of dense collection" which will be following this rule, as well.
REFERENCES:
To: Respondents to the Call for Comments, The Meteorite-list,
The Meteoritical Bulletin mailing list
From: Jeff Grossman, Chair, Nomenclature Committee
Dear all,
Last summer, I requested input from the community on two proposals under
consideration by the Nomenclature Committee (NomCom). The first would
change the rules by which meteorites from Morocco and surrounding areas
are named, allowing well-documented meteorites to receive names other than
Northwest Africa (NWA). The second would change the rules for naming
paired meteorites from dense collection areas.
I received many thoughtful comments from people representing all parts
of the meteorite community, including scientists, dealers, collectors,
and educators. These comments were reviewed by the NomCom, who, after
a rather long and complicated debate, have now revised the Guidelines
for Meteorite Nomenclature.
Here is what was done:
1) NWA ... +++++++++++
2) The rules for handling paired meteorites from dense collection areas
were not changed. Each new specimen will continue to receive a unique
number and be subject to the existing type-specimen requirements.
There was strong support in most parts of the meteorite community AND
on the NomCom
for changing these rules in some way that would allow the Committee to
recognize pairings, which in turn would reduce the type-specimen
requirements for certain paired meteorites. However, the Committee was
unable to devise a practical way to do this. Of particular concern
were potential legal consequences for scientists involved in disputed
pairing decisions and the high administrative burden that any new system
would place on the NomCom. The NomCom remains open to new ideas about
changing these rules, but for now there will be no change.
The revised Guidelines for Meteorite Nomenclature are online at
http://meteoriticalsociety.org/bulletin/nc-guidelines.htm.
Thanks to all of you who took the time to send me your opinions.
I apologize to those of you getting this message more than once...
there is significant overlap of the mailing lists I have to use.
Jeff
Dr. Jeffrey N. Grossman
Chair, Meteorite Nomenclature Committee (Meteoritical Society)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
Thanks to Rob Matson for his editing and review of this article.
The subject of California meteorites will be the topic of my future articles.
My previous articles can be found *HERE*
For more information, please contact me by email:
Bolide*chaser
